

- #Itchy rash on buttocks crack skin#
- #Itchy rash on buttocks crack Patch#
- #Itchy rash on buttocks crack full#
#Itchy rash on buttocks crack Patch#
They may recommend patch testing if it looks like you have contact dermatitis. They may also take a biopsy of the rash to figure out the cause.
#Itchy rash on buttocks crack skin#
They may scrape your skin to look for fungus or scabies.

#Itchy rash on buttocks crack full#
Your doctor will take a full medical history and physical exam. Avoid irritants (jewelry, etc) on the rash.Use only fragrance-free products on the skin.Anti-itch lotion (Sarna) or hydrocortisone cream.Take lukewarm showers and completely dry your skin.For more serious drug rashes, oral steroids may be needed. Prescription topical steroids can help with itching and making the rash go away faster.Īfter stopping the medication, it usually takes 10 to 14 days for the rash to completely go away.Īvoid taking this medication again in the future and let all of your doctors know about your reaction. Treatment for drug rashes include stopping the medication. If you also have a fever, facial swelling, swollen lymph nodes, skin blisters, skin pain, or ulcers on the mouth or genitals, seek emergency care. In rare cases, drug rashes can be life threatening. The rash appears as red bumps that spreads from the chest and back to the rest of the body. They occur 1 to 2 weeks after starting a new medication or increasing the dose of an existing medication. Usually starts 1 to 2 weeks after starting a new medication or increasing the dose of a medicationĭrug rashes are allergic reactions to medications, particularly antibiotics and blood pressure medications, or diuretics.Treatment may include an oral or topical antibiotic or a topical steroid lotion. If it does not improve or if it gets worse, see a dermatologist. OTC benzoyl peroxide wash can help treat bacterial folliculitis. Not shaving and avoiding skin-care products for several days can clear it up. Sometimes, folliculitis gets better on its own. The bumps can be painful, burning, or itchy. Instead of pus, there is often a clear liquid inside the bumps. It causes inflammation around the hair follicle, but there isn’t an infection. An irritant folliculitis occurs from repeated trauma of the hair follicle.
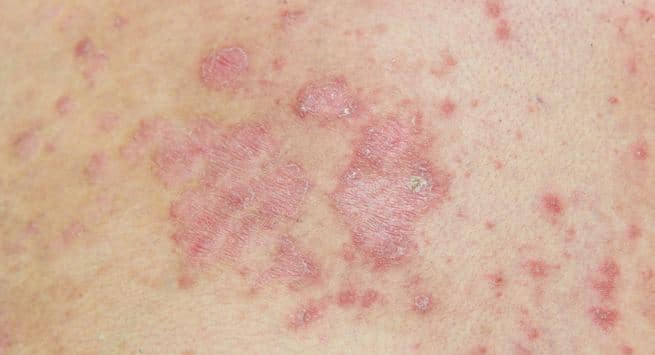
It causes the bumps, which are often filled with pus. The bacteria enters the hair follicles through open skin.

There are two main causes of folliculitis: an infection and an irritation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
